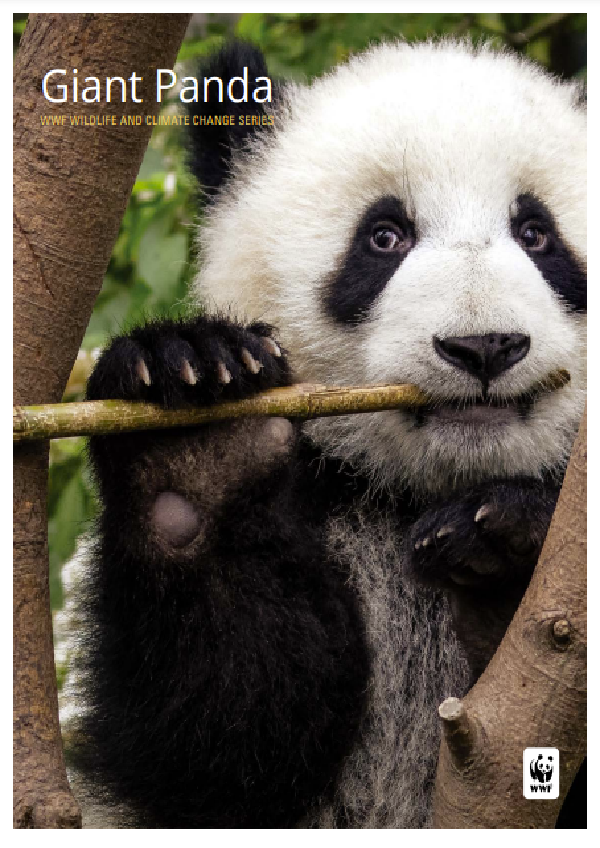
Tigers are the largest of all cats, but one of the most endangered species today. The number of wild tigers in the world once reached 100,000, but tiger poaching has become more and more rampant because the skin and bones of tigers can be made into valuable furs and medicinal materials. The habitat was gradually destroyed, causing the tiger population to plummet by more than 95%. Tigers play an important role in maintaining healthy ecosystems. At present, the number of wild tiger populations in the world is facing collapse. Tiger habitats now occupy 40% less than 10 years ago, and tigers only account for 7% of the historical range.
Threats facing tigers:
Lack of adequate food: A tiger needs a medium-sized deer for a week to survive, and when there is insufficient food, the tiger population will plummet. Too many forests in Asia have been classified as “empty forests”—even if there are trees, the animals inside are all gone. Therefore, anti-poaching patrols must target tigers and their prey populations.
Habitat loss: Tigers are endemic to Asia, where population booms require tigers to compete with humans for space in densely populated areas. The population pressures in the countries of origin of tigers such as India, Vietnam, and Bangladesh are very high, which greatly reduces the living space of tigers.
Illegal hunting: The beautiful fur of tigers has long been coveted by the market for carpets, ornaments, and furs, and tiger products such as tiger bones are also regarded as miraculous drugs, which has contributed to the perpetuation of illegal hunting. The conflict between tigers and protected area residents is also the reason for the hunting.
Threats to Genetic Diversity: Currently, most tiger populations have fewer than 100 individuals, and probably less than half of them are suitable for breeding. Inbreeding is common, and even “incestuous” breeding occurs from time to time. This leads to a decline in the genetic diversity and genetic quality of the population.
Natural disasters: Small and isolated tiger populations are extremely vulnerable to natural disasters. Forest fires, floods, storms, etc. caused by environmental degradation pose a great threat to tigers. At the same time, due to the decline of genetic quality, the ability of tiger populations to resist the spread of diseases is reduced, which greatly increases the destructive power of epidemic diseases on tigers.
Tigers are facing unprecedented threats, habitat loss and fragmentation, hunting and illegal wildlife trade, and the lack of policies to protect tigers. Tiger conservation absolutely needs global attention and action. We need to help rebuild their homes and keep their habitat from being destroyed. No one is allowed to steal. Enhance people’s awareness of tiger protection and improve the legal quality of the whole people. Let the tigers continue to thrive on earth.